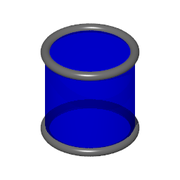
Cylinder (EntityTopic, 14)
From Hi.gher. Space
A cylinder is a special case of a prism where the base is a circle. it has two circles at the ends connected by a surface, called a hose.
Equations
- Variables:
r ⇒ radius of cylinder
h ⇒ height of cylinder
- All points (x, y, z) that lie on the surface of a cylinder will satisfy the following equations:
x2 + y2 = r2
abs(z) ≤ h/2
-- or --
x2 + y2 < r2
abs(z) = h/2
- All points (x, y, z) that lie on the edges of a cylinder will satisfy the following equations:
x2 + y2 = r2
abs(z) = h/2
- The hypervolumes of a cylinder are given by:
total edge length = 4πr
surface area = 2πr(r+h)
volume = πr2h
- The planar cross-sections (n) of a cylinder are:
[!x,!y] ⇒ rectangle with width (2rcos(πn/2)), height (h)
[!z] ⇒ circle of radius (r)
Homology groups
All homology groups are zero unless stated. Here X is the shape in the given frame, and nZ is the direct sum of n copies of the group of integers Z.
- 1-frame (two circles)
- H0X = 2ℤ, H1X = 2ℤ
- 2-frame (2 disks and a tube)
- H0X = ℤ, H1X = 0, H2X = ℤ
- 3-frame (solid cylinder)
- H0X = ℤ
Cylindrogram
A cylindrogram is the surface of revolution of a parallelogram, just as a cylinder is the surface of revolution of a rectangle. It can also be thought of as a cylinder with a cone removed from one end and placed on the other. As such, this shape has the same volume as a cylinder with the same radius and height.
| Notable Trishapes | |
| Regular: | tetrahedron • cube • octahedron • dodecahedron • icosahedron |
| Direct truncates: | tetrahedral truncate • cubic truncate • octahedral truncate • dodecahedral truncate • icosahedral truncate |
| Mesotruncates: | stauromesohedron • stauroperihedron • stauropantohedron • rhodomesohedron • rhodoperihedron • rhodopantohedron |
| Snubs: | snub staurohedron • snub rhodohedron |
| Curved: | sphere • torus • cylinder • cone • frustum • crind |
| 5. 3 Sphere | 6. 21 Cylinder | 7. 111 Cube |
| List of tapertopes | ||
| 2a. III Cube | 2b. (III) Sphere | 3a. (II)I Cylinder | 3b. ((II)I) Torus | 4a. IIII Tesseract | 4b. (IIII) Glome |
| List of toratopes | |||||
| 6. (III) Sphere | 7. [(II)I] Cylinder | 8. <(II)I> Bicone |
| List of bracketopes | ||